Ellipse
Pronunciation: /ɪˈlɪps/ Explain
|
A ellipse is a closed curve that can be represented by the equation 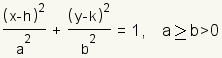 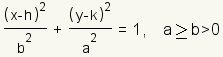 Something that is related to an ellipse or is in the shape of an ellipse can be called elliptic or elliptical. For example, elliptic geometry is a geometry that can be visualized as taking place on the surface of an ellipse. |
| Variable or Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| x | The variable x represents the horizontal axis. |
| y | The variable y represents the vertical axis. |
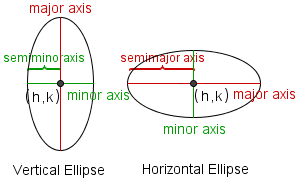
| a | The parameter a represents the length of the semimajor axis. |
| b | The parameter b represents the length of the semiminor axis. |
| h | The parameter h represents the x position of the center of the ellipse, which is at the intersection of the major axis and minor axis. |
| k | The parameter k represents the y position of the center of the ellipse, which is at the intersection of the major axis and minor axis. |
| Table 1 | |
Each ellipse has two axes, a major axis and a minor axis. Each axis is a line around which the ellipse is symmetrical. One is horizontal and the other is vertical. The major axis of an ellipse is the larger of the two axes. The major axis is also called the principal axis. The minor axis of an ellipse is the smaller of the two axes. Half the major axis is called the semimajor axis. Half the minor axis is called the semiminor axis. In the equation for the ellipse, a is the length of the semimajor axis, and b is the length of the semiminor axis. (h,k) is a point at the center of the ellipse. Changing h moves the ellipse to the left or right. Changing k moves the ellipse up or down. An ellipse is a conic section formed by intersecting a plane with a cone. |
Properties of an Ellipse
|
The
endpoints
of the horizontal axis are at
Each ellipse has two foci. Each focus can be found on the
major axis.
The eccentricity of an ellipse is a measure of how much it is changed from a circle. In the case where b = a, the ellipse is a circle and the eccentricity is 0. The formula for the eccentricity of an ellipse is 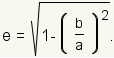 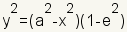 An ellipse can also be defined with one focus point and a directrix. An ellipse is all points such that the ratio of the distance from the focus to the point on the ellipse divided by the distance from the point on the ellipse to the directrix is equal to the ratio of c to a. |
Formulas Related to the Ellipse
| Name | Formula |
|---|---|
| Equation of an ellipse if the major axis is horizontal. | 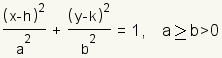 |
| Equation of an ellipse if the major axis is horizontal. | 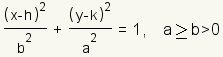 |
| Endpoints of the horizontal axis of a horizontal ellipse. | 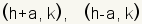 where c2 = a2 - b2 where c2 = a2 - b2 |
| Endpoints of the vertical axis of a vertical ellipse. | 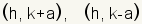 where c2 = a2 - b2 where c2 = a2 - b2 |
| Foci of a horizontal ellipse. | 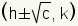 where c2 = a2 - b2 where c2 = a2 - b2 |
| Foci of a vertical ellipse. | 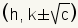 where c2 = a2 - b2 where c2 = a2 - b2 |
| Eccentricity of an ellipse. | 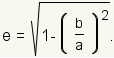 |
| Area of an ellipse. |  where a and b are the lengths of
the major and minor axes of the ellipse. where a and b are the lengths of
the major and minor axes of the ellipse. |
| The circumference of an ellipse is expressed using an infinite series. | ![C=2*pi*a[1-(1/2)^2*e^2-((1*3)/(2*4))^2*((e^4)/3))-((1*3*5)/(2*4*6))^2*((e^6)/5)-...]](../../equations/e/ellipseeqn34.png) where ε is the
eccentricity. where ε is the
eccentricity. |
| Table 2 - Formulas related to an ellipse. | |
Sketching an Ellipse
The general form of the elliptical equation is
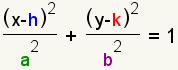 .
.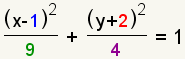 .
.| Step | Example | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 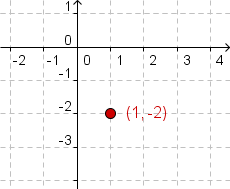 |
First, plot the center of the ellipse at
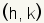 . In this example . In this example
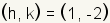 . .
For the x-coordinate, start with
For the y-coordinate, start with
|
| 2 | 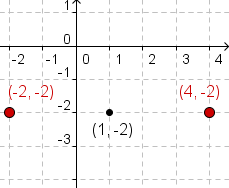 |
Now plot the endpoints of the horizontal axis. The left endpoint is at
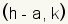 . In this
case that is . In this
case that is 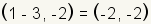 .
Plot the right endpoint at .
Plot the right endpoint at 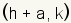 .
For this equation, .
For this equation, 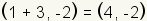 . .
|
| 3 | 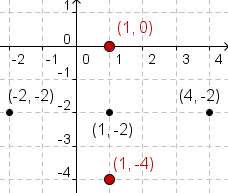 |
Now plot the endpoints of the horizontal axis. The bottom endpoint is at
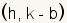 . In this
case that is . In this
case that is 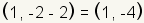 .
Plot the top endpoint at .
Plot the top endpoint at 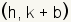 .
For this equation, .
For this equation,  . .
|
| 4 | 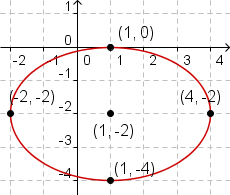 |
Now sketch the ellipse. |
| 5 | 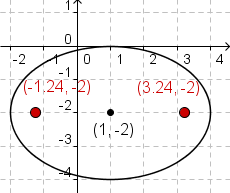 |
To plot the foci, calculate the value of c. The equation for c
is 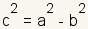 . Using
the values of a and b, . Using
the values of a and b,
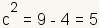 , and , and
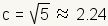 .
Since the major axis is the horizontal axis, the foci are at .
Since the major axis is the horizontal axis, the foci are at
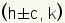 . Substituting the
values gives . Substituting the
values gives 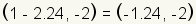 and
and 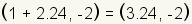 . .
|
| Table 2 | ||
References
- McAdams, David E.. All Math Words Dictionary, ellipse. 2nd Classroom edition 20150108-4799968. pg 68. Life is a Story Problem LLC. January 8, 2015. Buy the book
- Hustler, James Devereux. The Elements of the Conic Sections with the Sections of the Conoids. 3rd edition. pp 19-40. www.archive.org. J. Deighton and Sons. 1826. Last Accessed 7/9/2018. http://www.archive.org/stream/elementsofconics00hastuoft#page/19/mode/1up/search/ellipse. Buy the book
Cite this article as:
McAdams, David E. Ellipse. 4/20/2019. All Math Words Encyclopedia. Life is a Story Problem LLC. http://www.allmathwords.org/en/e/ellipse.html.Image Credits
- All images and manipulatives are by David McAdams unless otherwise stated. All images by David McAdams are Copyright © Life is a Story Problem LLC and are licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
Revision History
4/20/2019: Updated expressions and equations to match new format. (McAdams, David E.)12/21/2018: Reviewed and corrected IPA pronunication. (McAdams, David E.)
7/5/2018: Removed broken links, updated license, implemented new markup, implemented new Geogebra protocol. (McAdams, David E.)
1/7/2010: Added "References". (McAdams, David E.)
11/12/2009: Added table of formulas. (McAdams, David E.)
3/10/2009: Added definition of axis of an ellipse. (McAdams, David E.)
12/10/2008: Initial version. (McAdams, David E.)
- Navigation
- Home
- Contents
-
# A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z - Teacher Aids
- Classroom Demos
- How To
- LIASP
- LIASP Home
- Conditions of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Donate to LIASP
- Help build this site
- About LIASP
- Contact LIASP
All Math Words Encyclopedia is a service of
Life is a Story Problem LLC.
Copyright © 2018 Life is a Story Problem LLC. All rights reserved.
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License

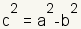 .
The foci are
two points on the major axis of the ellipse. For each point in the ellipse, the sum
of the distance of that point to the foci is equal to
.
The foci are
two points on the major axis of the ellipse. For each point in the ellipse, the sum
of the distance of that point to the foci is equal to
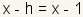 . Now subtract
x from both sides to get
. Now subtract
x from both sides to get
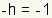 . Multiply both
sides by
. Multiply both
sides by 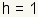 .
.
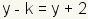 . Now subtract
y from both sides to get
. Now subtract
y from both sides to get
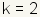 . Multiply both
sides by
. Multiply both
sides by